葛蔚团队最新研究进展
徐骥:
基于原创的介科学理论,突破复杂颗粒体系粗粒化、大规模异构并行计算、反应传递多过程耦合等难题,自主研制出多相系统多尺度离散模拟软件DEMms。与国外竞品ANSYS Fluent相比,颗粒计算的规模高两个量级以上,计算速度快一个量级以上,可更精确计算颗粒间受力,在化工、冶金、医药等领域工程设计与优化应用测试中表现出良好适用性。

多尺度多相系统离散模拟软件DEMms
代表文章:
[1] Ji Xu,Peng Zhao,Yong Zhang,Junwu Wang,Wei Ge*,Discrete particle methods for engineering simulation: Reproducing mesoscale structures in multiphase systems,Resources Chemicals and Materials,2022,1: 69–79.
[2] Zhipeng Xiong,Huihuang Xia,Ji Xu*,Chunjiang Liu*,Wei Ge,A dual-grid approach for CFD–DEM simulation of gas–solid heat transfer,AIChE Journal,2025,e18899
[3] Aiqi Zhu,Qi Chang,Ji Xu*,Wei Ge*,A dual-grid approach to speed up large-scale CFD-DEM simulations. Chemical Engineering Journal,2024,492: 152218
引用文章:
[1] Musango Lungu,Jingdai Wang,Yongrong Yang,On fluidization dynamics of Geldart D particles,Powder Technology 459 (2025) 121014
[2] Dazhao Gou,Yansong Shen,GPU-powered CFD-DEM framework for modelling large-scale gas–solid reacting flows (GPU- rCFD-DEM) and an industry application,Chemical Engineering Science 299 (2024) 120536
[3] Mengyuan Wang,Kai Huang,Rui Liu,Xinhao Li,Yuxuan Liu,Yifan Liu,Chunlei Pei,and Jinlong Gong. Numerical analysis of transient gas-solid flow in a non-mechanical L-valve,Chemical Engineering Science 313 (2025):121769
侯超峰:
研究团队创建了大规模高性能原子模拟方法,取得了巨大的性能加速,支持千万计算核心的高效并行计算,模拟原子数目超过万亿[1,2,4,6]。克服了纳微结构热力学性质非平衡分子动力学模拟的有限尺寸效应,揭示了纳微尺度声子传递机制,建立了介尺度导热模型[3,7,8]。以此建立了集成诸多纳微因素的芯片电路热模拟技术[5],形成了自主大规模高性能软件,在多台全球第一中国超算系统实现了全机规模应用,为芯片热管理设计提供了有力手段。
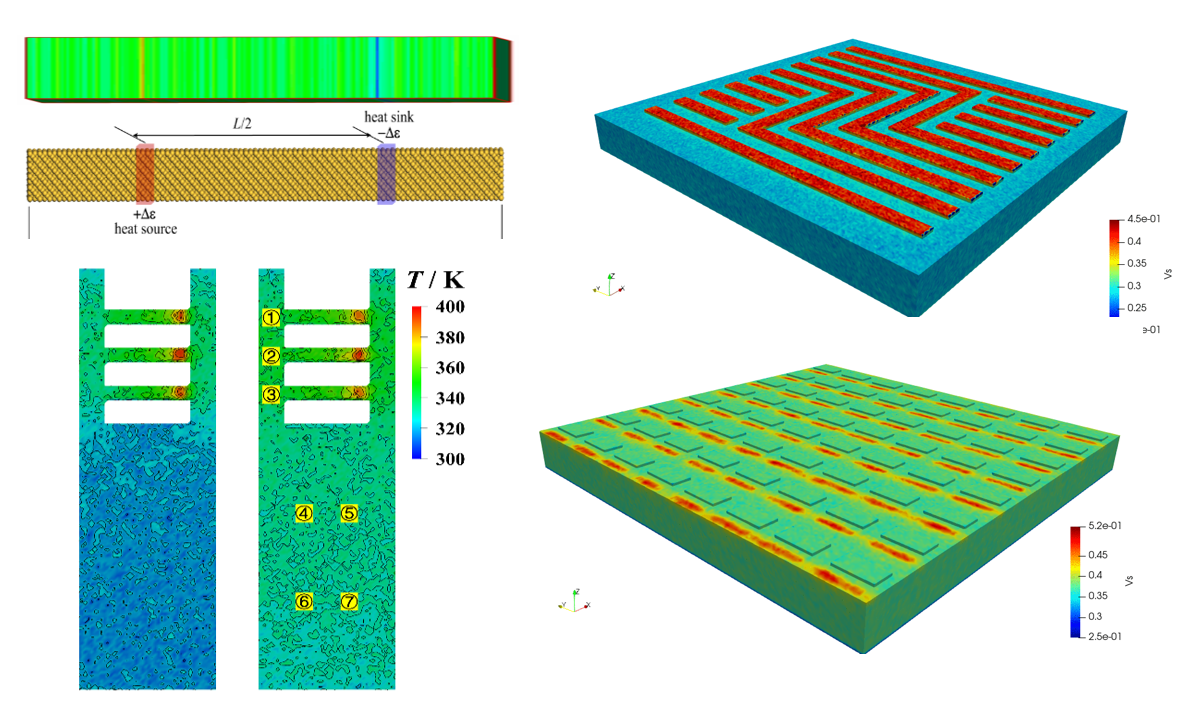
代表文章:
[1] Yufeng Huang,Chaofeng Hou*,Wu Li,Gang Zhang and Wei Ge,Size-Dependent Thermal Conductivity of Thick Low-Dimensional Silicon Nano-Structures,The Journal of Physical Chemistry C,2025,129,13813−13821.
[2] Chenyang Sun,Chaofeng Hou*,Wei Ge,Yaning Zhang*,A prediction model for thermal conductivity of supercritical carbon dioxide,AIChE Journal,2025,e18824,1-6.
[3]. Hou Chaofeng*,Zhu Aiqi,Zhao Mingcan,Zhang Shuai,Ye Yanhao,Huang Yufeng,Xu Ji,Ge Wei*,Atomistic simulation toward real-scale microprocessor circuits,Chemical Physics Letters,2022,791:139389.
引用文章:
[1]. Chaofeng Hou,Ji Xu,Peng Wang,Wenlai Huang,Xiaowei Wang,Wei Ge*,Xianfeng He,Li Guo,Jinghai Li,Petascale molecular dynamics simulation of crystalline silicon on Tianhe-1A. International Journal of High Performance Computing Applications,27(2013),307-317.
[2]. Chaofeng Hou*,Ji Xu,Peng Wang,Wenlai Huang,Xiaowei Wang,Efficient GPU-accelerated molecular dynamics simulation of solid covalent crystals. Computer Physics Communications,184(2013),1364-1371.
[3].Chaofeng Hou*,Ji Xu,Wei Ge*,Jinghai Li,Molecular dynamics simulation overcoming the finite size effects of thermal conductivity of bulk silicon and silicon nanowires. Modelling and Simulation in Materials Science and Engineering,24,045005,2016.
[4]. Chaofeng Hou*,Zhang Chenglong,Wei Ge,Wang Lei,Han Lin,Pang Jianmin,Record Atomistic simulation of crystalline silicon: bridging microscale structures and macroscale properties. Journal of Computational Chemistry,41,731-738,2020.
[5]. Chaofeng Hou*,Aiqi Zhu,Mingcan Zhao,Shuai Zhang,Yanhao Ye,Yufeng Huang,Ji Xu,Wei Ge*,Atomistic simulation toward real-scale microprocessor circuits,Chemical Physics Letters 791,139389,2022.
[6]. Chaofeng Hou*,Aiqi Zhu,Mingcan Zhao,Shuai Zhang,Yanhao Ye,Ji Xu,Wei Ge,Atomistic Simulation of Low-Dimensional Nanostructures toward Extreme-Scale Supercomputing,CCF Transactions on High Performance Computing,5,3-11,2023.
[7]. Yufeng Huang,Chaofeng Hou*,Wei Ge,Lattice Boltzmann method with effective correction of phonon properties for nano/microscale heat transfer,Physica Scripta,2022,97:115703.
[8]. Yufeng Huang,Chaofeng Hou,* Wu Li,Gang Zhang and Wei Ge,Size-Dependent Thermal Conductivity of Thick Low-Dimensional Silicon Nano-Structures,The Journal of Physical Chemistry C,129,13813−13821,2025.
李成祥:
采用自主开发的硬球-拟颗粒(HS-PPM)耦合方法,针对吸附剂的吸附速率与容量难以兼顾的难题,模拟了孔道内吸附-扩散耦合过程,揭示吸附性能瓶颈,并建立多组分扩散系数预测模型。通过精准调控孔径分布,实现了吸附速率与容量的协同提升,并通过实验验证了该优化效果,模拟方法可进一步推广至催化反应等相关系统的优化设计中。
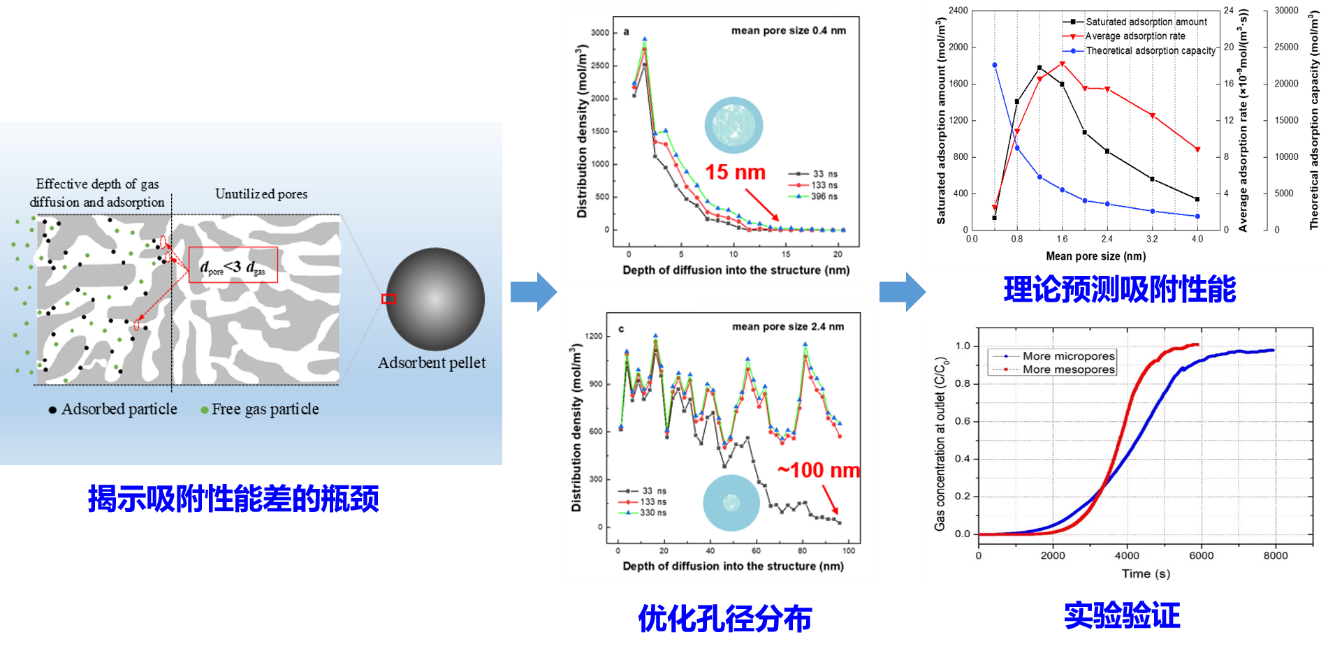
高性能吸附剂吸附-扩散耦合模拟及结构优化设计
代表文章:
[1] Yifan Zhu,Tianhao Qiu,Tingting Liu,Chengxiang Li*,Ying Huai,Wei Ge*,Simulation of gas diffusion-adsorption coupling in adsorbents for optimizing pore structures, Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,2024,63:17402-17412.
[2] Tianhao Qiu,Chengxiang Li*,Yaning Zhang,Wei Ge*,HS-PPM simulation for diffusion coefficients of binary and multi-component gas mixtures, AIChE Journal,2025,71 (9):e18891.
[3] Haolei Zhang,Mingcan Zhao,Yanping Li,Chengxiang Li*,Wei Ge*,Concentration fluctuation caused by reaction-diffusion coupling near catalytic active sites,Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering,2022,50: 254-263.
引用文章:
[1] Chengxiang Li,Ji Xu,Tianhao Qiu,Zikang Sun,Haolei Zhang,Wei Ge*,Trans-level multi-scale simulation of porous catalytic systems: bridging reaction kinetics and reactor performance,Chemical Engineering Journal,2023,455:140745.
[2] Tianhao Qiu,Mingcan Zhao,Yanping Li,Chengxiang Li*,Wei Ge,Multiscale Modeling of Gas–Solid Surface Interactions Under High-Temperature Gas Effect,Journal of Thermophysics and Heat Transfer,2022,36:951-963.
张勇:
颗粒-流体系统中微尺度到宏尺度存在明显的时空间隔,时间多尺度动态模拟方法基于介尺度结构动态演化机制,采用多时间步长递进演化,耦合直接数值模拟、粗粒化模型、稳态模型等不同方法在精度、速度的优势,可以实现工业装备长时间、大规模高效计算,并在煤炭分选、多晶硅冷氢化加工、石油焦化等过程应用。
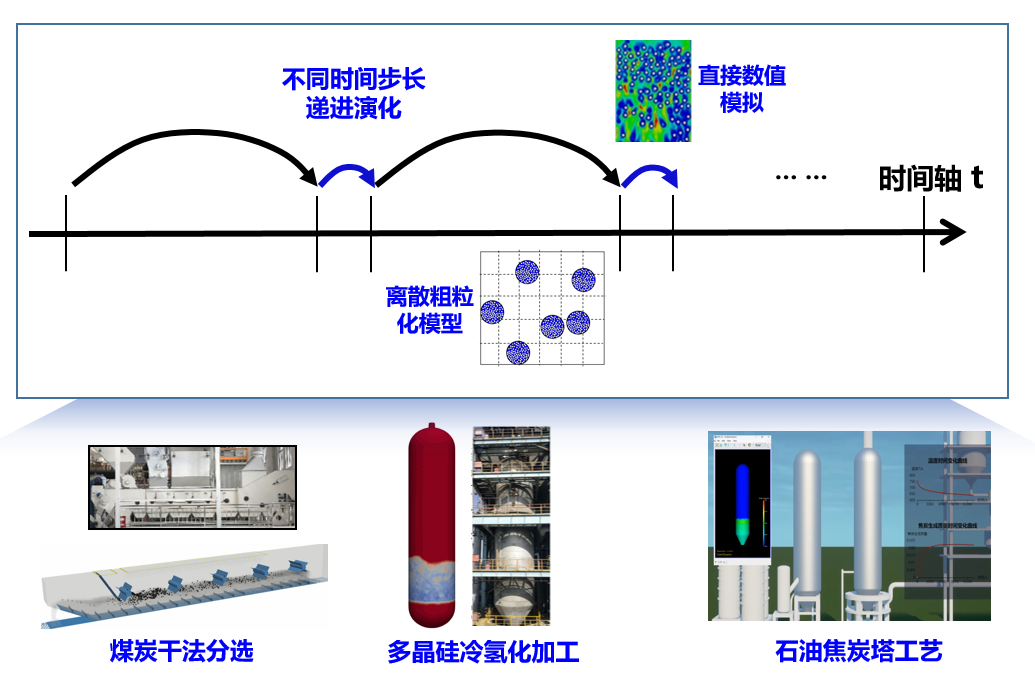
时间多尺度动态模拟方法及其应用
引用文章:
[1] Zhang Y*,Xu J,Chang Q,Ge W*. Bi-layer coarse-grained DPM of gas-solid systems with mesoscale heterogeneity resolved. Chemical Engineering Science 2022;263: 118058.
[2] Jia Y,Zhang Y*,Han W,Xiong X,Zhou E,Xu J,Duan C*,Feng Y,Zhao Y,Ge W. Multiscale modelling and simulation of coal separation process in a pilot-scale gas–solid fluidized bed. Chemical Engineering Journal 2025;511: 161912.
[3] Han W,Yue Y,Jia Y,Xiong X,Zhang Y*,Liu Y,Wang L,Cao Y*,Ge W,Dynamically coupling computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and steady-state model (SSM) for simulating industrial coke drum and temperature prediction. Chemical Engineering Science 2026;320: 122678.
陈飞国:
曳力系数(CD)是颗粒-流体系统的重要基本参数。采用结合时间驱动算法与硬球模型的拟颗粒模拟方法(PPM),研究了1≤Re≤20和0.1≤Ma≤3条件下孤立颗粒及颗粒阵列的绕流问题,分析了曳力系数与雷诺数(Re)、马赫数(Ma)及固相体积分数(εs)之间的关系。研究表明:1)曳力系数随Re和Ma的增大而减小,其关系式为CD (Re,Ma)= CD (Re)[aexp(-bMa)+(1-a)],其中CD(Re)为不可压缩流中孤立颗粒的标准阻力系数,系数a、b与Re相关;2)曳力系数随εs增大而增大,其关系式为CD (Re,Ma,εs)= CD (Re,Ma)(1+Kεsn),系数K、n与Re和Ma相关。本研究填补了滑移流与过渡流区域内多颗粒曳力数据的空白,为广泛存在的颗粒-流体系统提供了曳力定律。
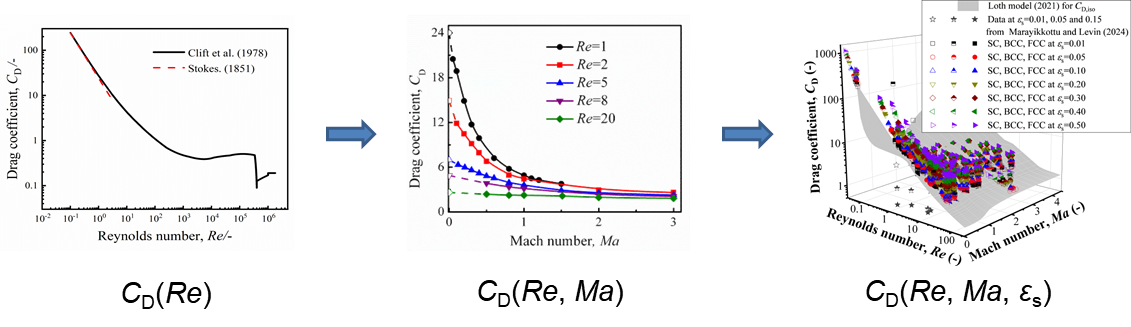
高马赫数低雷诺数条件下颗粒及颗粒阵列绕流曳力系数
文章:
1. Feiguo Chen *,Wei Ge. General drag correlations for subsonic to supersonic flow past ordered particle arrays at low and moderate Reynolds numbers. Computer and Fluids,2024,278:106324.
2. 龙凯,陈飞国*,熊勤钢*. 2025. 低雷诺数高努森数下的双圆柱绕流阻/升力系数. 化工进展, 2025,44(8):4526-4535.
引用文章:
1. 李瑞元,陈飞国,葛蔚,张永民. 2021. 高马赫数低雷诺数条件下圆球绕流曳力系数. 空气动力学学报,2021,39(3):201-208.
2. Loth E,Tyler Daspit J,Jeong M,et al. Supersonic and hypersonic drag coefficients for a sphere. AIAA Journal,2021,59(8):3261-3274.
3. Marayikkottu A V,Levin D A. Kinetic modeling of fluid-induced interactions in compressible,rarefied gas flows for aerodynamically interacting particles. International Journal of Multiphase Flow,2024,171: 104684.
张帅:
系列工作1:颗粒卸料波动行为的多尺度研究
针对移动床卸料过程,以连续两个颗粒流出的时间间隔为对象,高分辨率表征波动行为。发现了卸料过程的双峰分布特征及对应的两种控制机制。发现了颗粒落料过程的暂时性堵塞现象及发生机理,揭示了堵塞-自发坍塌现象的力学结构特征和能量演化特征,为料仓、移动床等设备稳定卸料提供了理论指导。
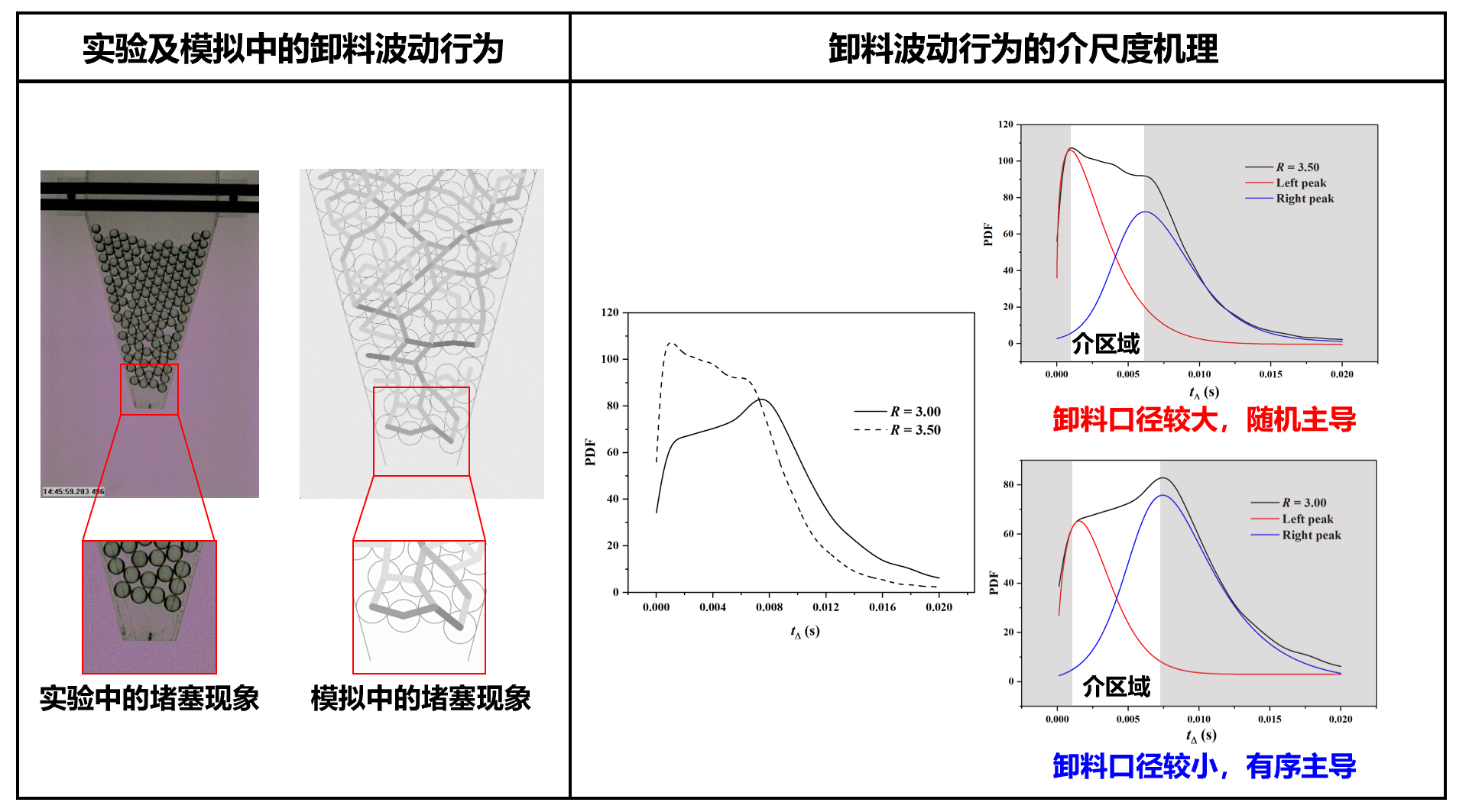
对应文章:
[1] Zhang,S.,Zhao,M.,Ge,W.,& Liu,C. (2021). Bimodal frequency distribution of granular discharge in 2D hoppers. Chemical Engineering Science,245,116945.
[2] Zhang,S.,Ge,W.,Chen,G.,Liu,Z.,Liu,T.,Wen,L.,& Liu,C. (2022). Numerical investigation on the clogging-collapsing events in granular discharge. Powder Technology,408,117714.
系列工作2:颗粒系统的多尺度耦合模拟研究
针对稠密颗粒系统,将具有精度优势的离散元方法与具有速度优势的连续介质方法在时间尺度耦合,在提高模拟结果空间分辨率的同时,相比离散元提速11倍。针对气固颗粒系统,基于计算域稀密相分解,将精确解析颗粒接触的离散颗粒模型与简化处理碰撞的多相质点网格法耦合,在鼓泡床模拟中提速35%。
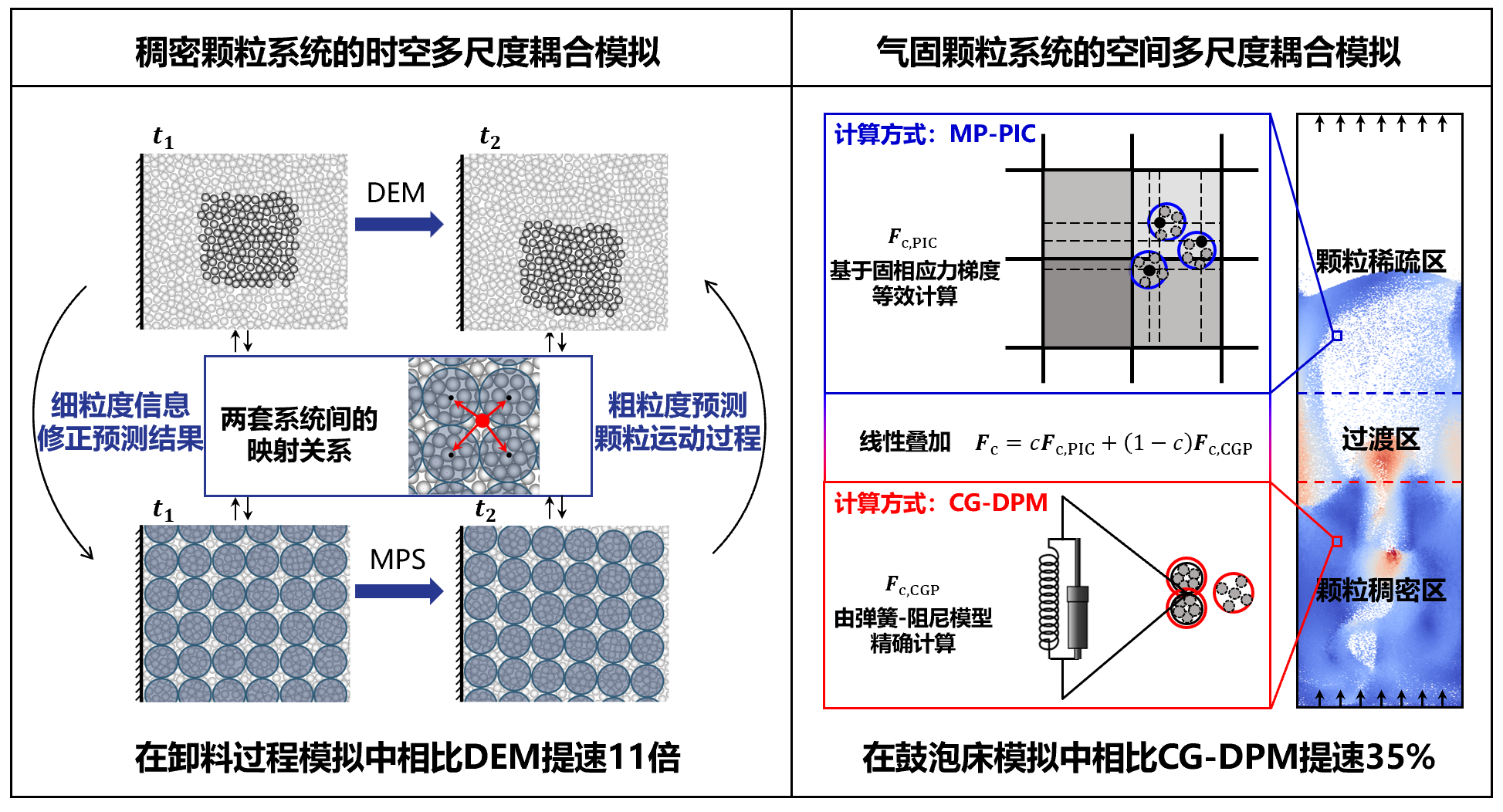
对应文章:
[1] Zhang,S.,Ge,W.,& Liu,C. (2023). Spatial–temporal multiscale discrete–continuum simulation of granular flow. Physics of Fluids,35(5).
[2] 张帅,徐嘉宇,华蕾娜,葛蔚,气固系统的CG-DPM与MP-PIC耦合模拟方法,2025,DOI: 10.11949/0438-1157.20250599
王媛:
研究用边界数据浸入法结合自适应网格加密模拟流固耦合,针对可压缩流中高阶格式需宽平滑区域降精度问题,在界面附近改用低阶格式并加密网格。经槽道流、圆柱绕流验证精度效率,又模拟Ma=2.67、Re=1482下激波驱颗粒,揭示曳力系数演化,为相关模拟提供新方法。
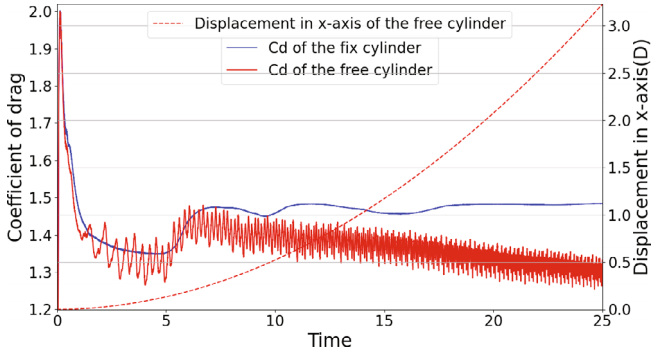
图1 固定颗粒(蓝线)和自由运动颗粒(红线)的曳力系数,以及自由颗粒在x方向的位移(红虚线)随时间的变化。
文章:
[1] Wang Y , Ge W .Simulation of fluid-structure interaction using the boundary data immersion method with adaptive mesh refinement[J].International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids, 2024, 96(7):14.DOI:10.1002/fld.5283.